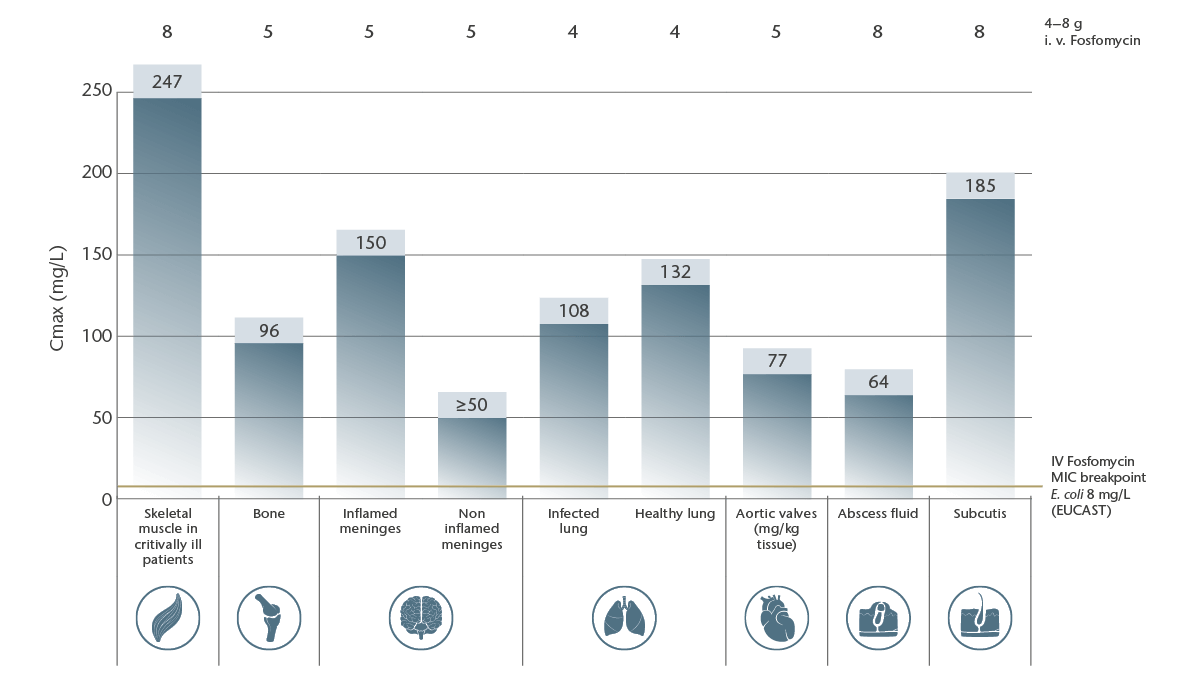
High bactericidal IV Fosfomycin levels at sites of infection
Excellent penetration with established dosage regimes into various compartments including tissues with poor accessibility such as skin and soft tissues, muscle, lung, bone, eye, heart, prostate and abscesses, as well as body fluids such as pleural effusions, cerebrospinal fluid and bile 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12.
Drug levels of IV Fosfomycin in different tissues
1 Joukhadar C, Klein N, Dittrich P, Zeitlinger M, Geppert A, Skhirtladze K, Frossard M, Heinz G, Müller M. Target site penetration of fosfomycin in critically ill patients. J Antimicrob Chemother 2003; 51: 1247–1252.
2 Matzi V, Lindenmann J, Porubsky C, Kugler SA, Maier A, Dittrich P, Smolle-Jüttner FM, Joukhadar C. Extracellular concentrations of fosfomycin in lung tissue of septic patients. J Antimicrob Chemother 2010; 65: 995–998
3 Schintler MV, Traunmüller F, Metzler J, Kreuzwirt G, Spendel S, Mauric O, Popovic M, Scharnagl E, Joukhadar C. High fosfomycin concentrations in bone and peripheral soft tissue in diabetic patients presenting with bacterial foot infection. J Antimicrob Chemother 2009; 64: 574–578
4 Radda TM, Gnad HD, Paroussis P. Fosfomycin levels in human aqueous humor after intravenous administration. Arzneimittelforschung 1985; 35: 1329–1331
5 Hirt SW, Alken A, Muller H, Haverich A, Vomel W. Perioperative preventive antibiotic treatment with fosfomycin in heart surgery: Serum kinetics in extracorporeal circulation and determination of concentration in heart valve tissue. Z Kardiol 1990; 79: 615–620
6 Takasaki N, Ra S, Okada S, Sakakibara T, Tonami H, Kitagawa Y, Miyazaki S. Transference of antibiotics into prostatic tissues: sampling method by transurethral resection for the measurement of the concentration of antibiotics in prostatic tissue. Hinyokika Kiyo 1986; 32: 969–975.
7 Sauermann R, Karch R, Langenberger H, Kettenbach J, Mayer-Helm B, Petsch M, Wagner C, Sautner T, Gattringer R, Karanikas G, Joukhadar C. Antibiotic abscess penetration: fosfomycin levels measured in pus and simulated concentration-time profiles. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2005; 49: 4448–4454
8 Lastra CF, Marino EL, Barrueco M, Gervos MS, Gil AD. Disposition of phosphomycin in patients with pleural effusion. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1984; 25: 458–462
9 Pfausler B, Spiss H, Dittrich P, Zeitlinger M, Schmutzhard E, Joukhadar C. Concentrations of fosfomycin in the cerebrospinal fluid of neurointensive care patients with ventriculostomy-associated ventriculitis. J Antimicrob Chemother 2004; 53: 848–852
10 Kuhnen E, Pfeifer G, Frenkel C. Penetration of fosfomycin into cerebrospinal fluid across non-inflamed and inflamed meninges. Infection 1987; 15: 422–424
11 Wittmann DIH. Chemotherapeutic principles of difficult-to-treat infections in surgery: II. Bone and joint infections. Infection 1980; 8: 330–333
12 Nakamura T, Hashimoto I, Sawada Y, Mikami J, Bekki E. Clinical studies on fosfomycin sodium following intravenous administration (tissue concentration and clinical efficacy) Jpn J Antibiot 1985; 38: 2057–2067
